Intrinsic motivation for robotic manipulation learning with sparse rewards
Intrinsic motivation for robotic manipulation learning with sparse rewards - Study of the impact of curiosity and intrinsic motivation as an exploration strategy for deep reinforcement learning agents on sparse-reward robotic manipulator environments.
Machine Learning Algorithms have become increasingly efficient at solving complexreal-world problems. In particular, Reinforcement Learning algorithms are capable of learning behaviors applicable to robotics that can replace or work together with classical control models, thereby increasing their robustness, applicability and viability. However,it remains difficult to design reward functions that represent, for a reinforcement learning agent, the task it must perform. Recent research in this area proposes techniques such as curiosity and intrinsic motivation as an alternative to the use of extrinsic environmental rewards, proving to be efficient in guiding the agent to satisfactory exploration in game environments such as VizDoom and Super Mario Bros. This paper analyzes the impact of the intrinsic motivation technique on agent training in robotic simulation environments, as well as its general implications for aspects such as generalization, exploration and sampling efficiency. We found that this approach encourages increasing exploratory behaviors even after the goal tasks were learned. Furthermore, we found that adding information about other objects' states into the agent's observation is crucial for learning complex behaviors when no dense reward signal is provided. This, however, requires the agent to learn it's own dynamics before interacting with the rest of the environment.



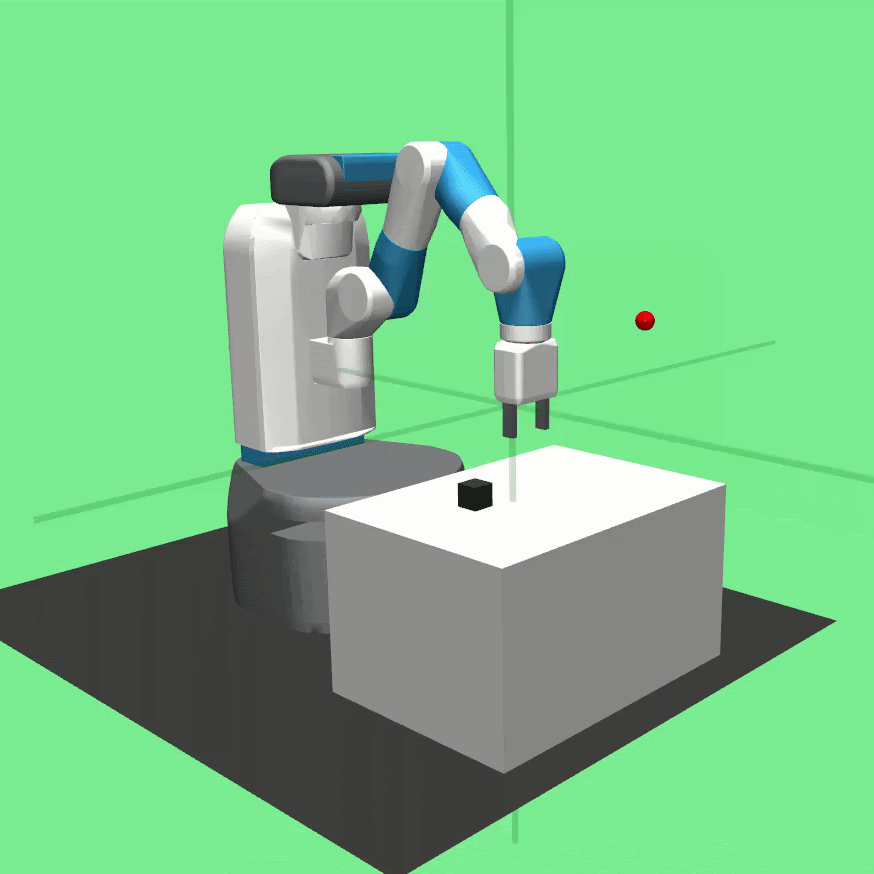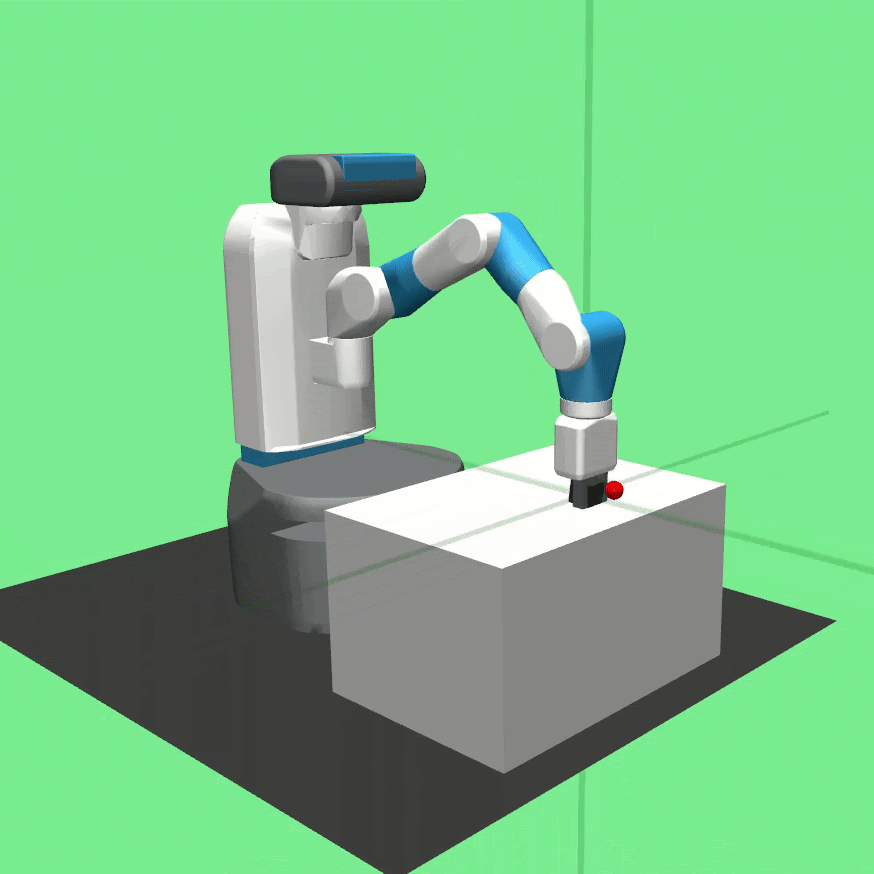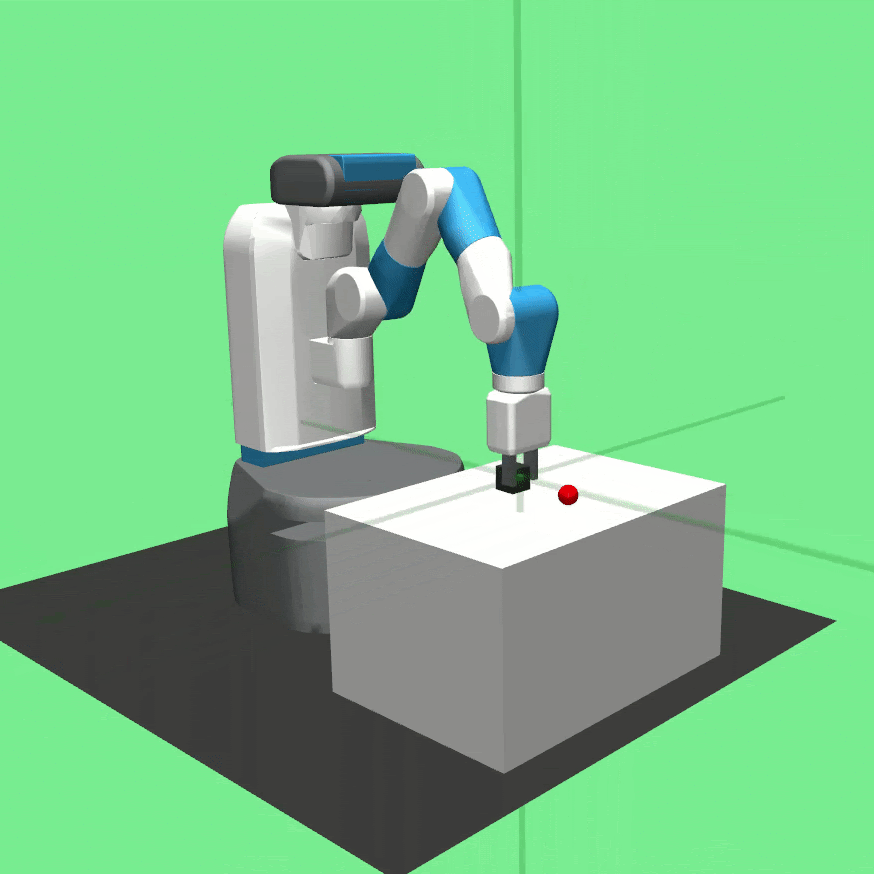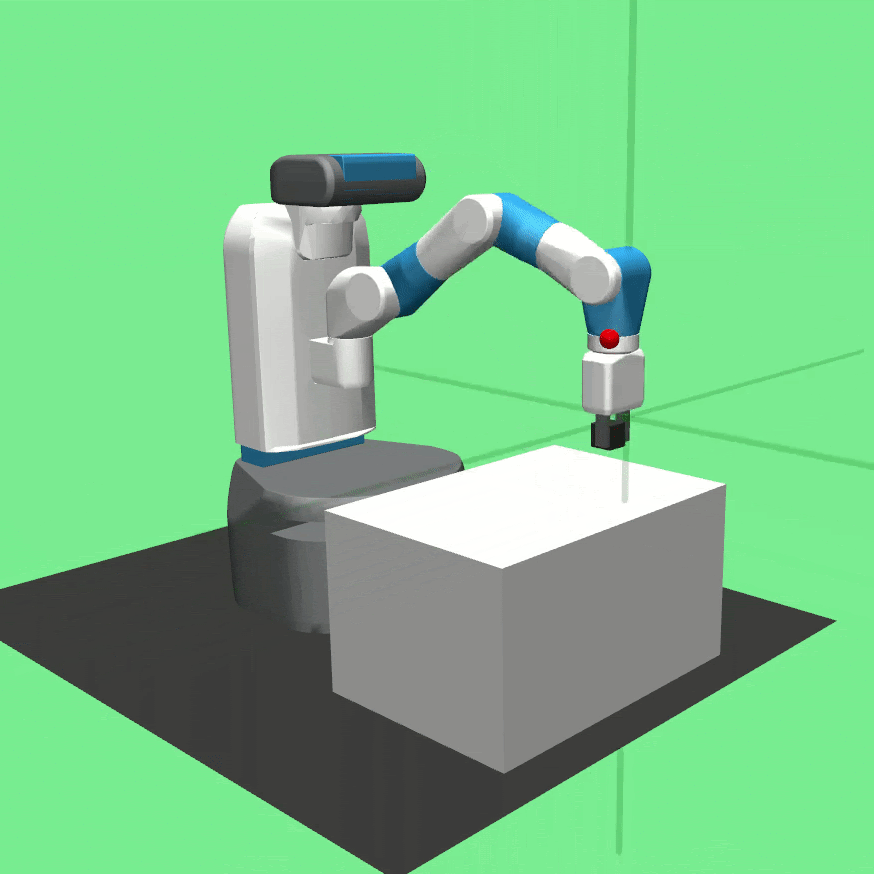
Learned policies for the tasks Pick And Place (left), Push (center) and Reach (right).
To read the full report, click here (Portuguese).
This study was inspired by the Robot open-Ended Autonomous Learning competition. The theoretic background was mainly based on
- Curiosity-driven Exploration by Self-supervised Prediction
- Large-Scale Study of Curiosity-Driven Learning
Success Rate Charts
Pick And Place Task (left), Push Task (center) and Reach (right). Blue lines are results for vanilla PPO (baseline) and red lines for PPO + intrinsic motivation.



Entropy Charts
Pick And Place Task (left), Push Task (center) and Reach (right). Blue lines are results for vanilla PPO (baseline) and red lines for PPO + intrinsic motivation.



Intrinsic Reward Charts
Pick And Place Task (left), Push Task (center) and Reach (right).


